Mail filtering nowadays
Rspamd has been started to handle mail flows that has grown over the last decade by more than ten times. From its inception, Rspamd has been tailored to address the demands of high-traffic mail systems, with a primary focus on optimizing performance and scanning speed. This advanced spam filtering system is written in plain C language and employs numerous techniques to operate efficiently, particularly on contemporary hardware. On the other hand, it is possible to run Rspamd even on an embedded device with a very constrained environment.
You can also check the recent performance analyse article to have a better impression about how fast Rspamd could be.
Rspamd can be regarded as a significantly faster alternative to the SpamAssassin mail filter, with the capability to process ten times the number of messages while using the same rules (via the SpamAssassin plugin). The following graph illustrates how the transition from SA to Rspamd has reduced CPU loads on scanning machines:
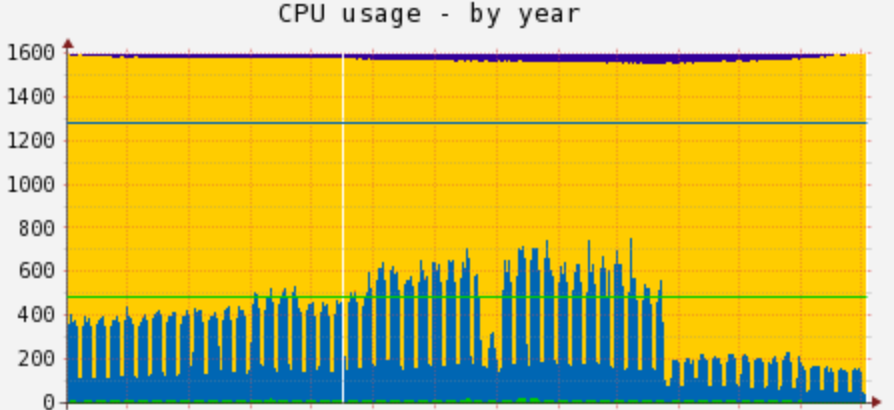
For faster email processing, Rspamd uses a set of global and local optimization techniques.
Global optimizations
Global optimizations are employed to enhance the overall message processing, improving the performance of all filters and organizing checks in an optimal sequence.
- Event-driven architecture enables Rspamd to execute network and other time-consuming requests concurrently in the background, enabling the processing of other messages while awaiting responses:
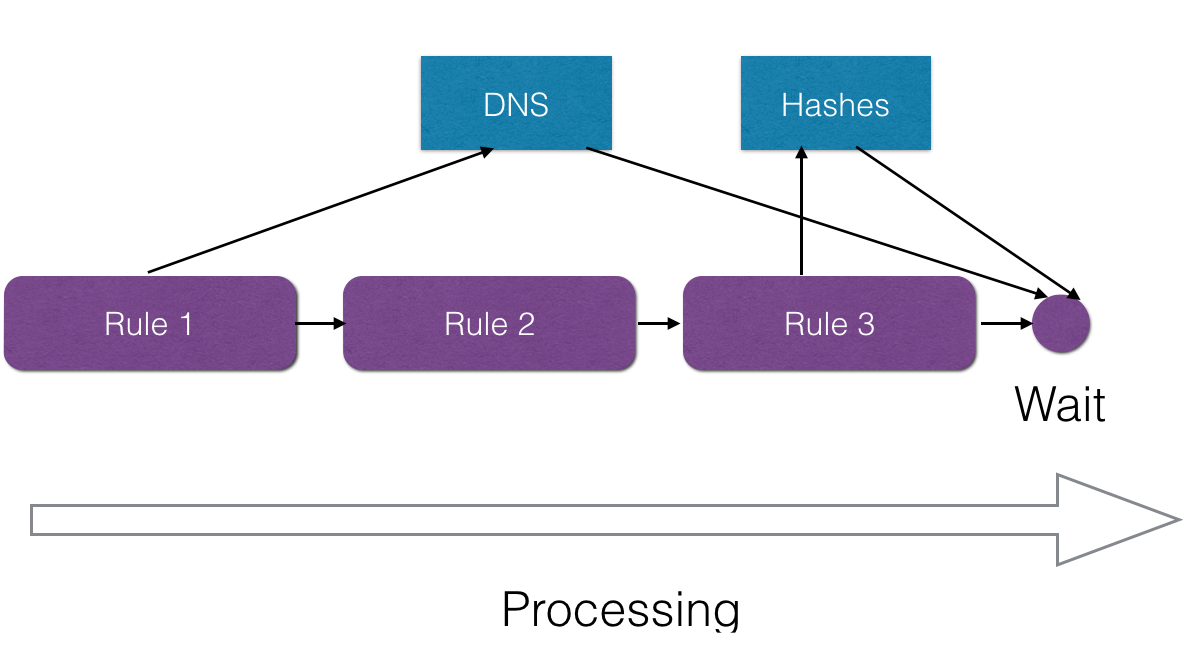
- Rules reordering is implemented to reduce message processing time. Rspamd prioritizes the inspection of rules with higher weight, shorter execution time, and a higher hit rate. Furthermore, Rspamd ceases processing when a message surpasses the spam threshold since additional checks are probably unnecessary.
Local optimizations
Rspamd employs various techniques to enhance the efficiency of each individual message processing stage. These improvements are achieved through the application of local optimization methods:
-
AST optimizations are employed to eliminate redundant checks from rules. You can delve into further details about this technique by perusing these slides.
-
In contrast to SA, Rspamd utilizes specific state machines for parsing email components such as MIME structures, HTML elements, URLs, images, received headers, and more. This approach allows for the swift extraction of information from emails, bypassing unnecessary details, rather than relying on an extensive array of regular expressions for these tasks.
-
The Rspamd system harnesses the Hyperscan engine to process extensive sets of regular expressions expeditiously. Unlike traditional regex engines, Hyperscan can process multiple expressions simultaneously. You can explore the finer intricacies of Hyperscan through these informative slides.
-
Assembly snippets are utilized to optimize specific algorithms for targeted architectures. Rspamd leverages assembly for frequently used cryptography and hashing algorithms. It selects the appropriate code version at runtime, based on CPU instruction set support tests.